CLASS I PROTECTION
1,984 ha
Ranau
14.03.1984
29/5C
99194506
None
Protection
Community Conservation Area & Water catchment (Pekan Nabalu)
Last updated: 20th June 2022
The FR is located within the Ranau district, 90 km east from Kota Kinabalu and 30 km from Ranau town, towards Kinabalu Park. The FR is accessible from the Kota Kinabalu-Ranau main road in the north and Tenompok-Toboh secondary road in the east.
Latitude/Longitude: 5° 56.777’N–6° 1.346’N; 116° 29.369’E 116° 32.606’E
Several structures are found within the northern part of the FR and they are as follows:
Creations – The reserve was classified as Class I Protection Forest in 1984. An overlap forested area of 760 ha occurred on the eastern part of the FR with Kampung Bundu Tuhan Native Residence Reserve that was gazetted by the His Most Excellency (Tuan Yang Terutama) in 1983. The current disputed area is called Winokok Conservation Area and is under the purview of the Bundu Tuhan Board of Trustees. Discussion to solve the disputed area is in progress.
Management responsibility – Ranau District Forestry Office
Boundary matters – The boundary is partially demarcated. The boundary within the disputed area is yet to be demarcated.
Management plan – None
Current Use – Protection and Research
Settlements and other buildings approximately 2 km from the boundary:
The FR is surrounded by private land which is mostly utilised for community-used forest area (Winokok Conservation Area), agricultural purposes and settlements.
Topography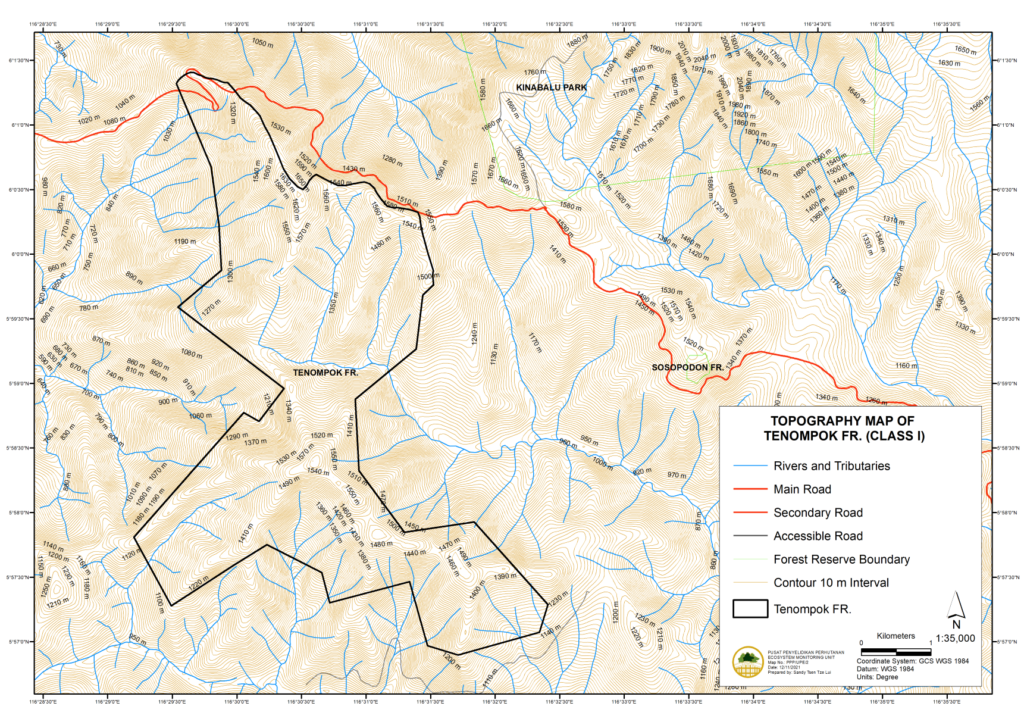
Figure 1: Topography and drainange map of Tenompok FR
Most of the FR is mountainous with slope amplitudes in excess of 300 m and normally greater than 25°. Ridge crest and valley bottoms are narrow and landslips are common. Sedimentary rock underlies most of the FR, which is formed from interbedded sandstone and mudstone.
Hydrology
River tributaries:
The reserve is well drained due to its mountainous terrain and serve as a water catchment for three rivers. The Lidan and Kenipir Rivers merge and become one of the tributaries of Labuk river, and Tomis river which is one of the tributaries of Tuaran river.
Soils
Crocker and Trusmadi soil associations.
Meteorological data
See Ranau Agriculture Station and Dallas rainfall data.
The forest type of this FR is largely lower montane forest. Most of the forest in Tenompok FR has been exposed to anthropogenic disturbances, due to the presence of numerous villages established in the adjacent area. The adjacent area has been exposed to swidden agricultural systems (also known as shifting cultivation), rotational farming in which land is cleared by fire, cultivated and then left to regenerate after a few years. This farming method has been practised for decades. The peripheral of the reserve, especially the northern and southern parts, were degenerated into low diversity and structured secondary vegetation.
Flora
A total of 544 plant taxa were recorded from the reserve. The ten most speciose families in decreasing order are Lauraceae (30); Rubiaceae (30); Fagaceae (21); Primulaceae (21); Moraceae (17); Orchidaceae (15); Araceae (14); Melastomataceae (14); Myrtaceae (13); and Gesneriaceae (11). Of which 147 are endemics to Borneo, including 31 endemics to Sabah.
Threatened species under IUCN Red List:
Taxa under Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: –
Schedule 1, part II – (i) Tetrastigma dichotomomum
Schedule 2, part II – (i) 15 Orchid (ii) 7 Gingers (iii) Ramin (iv) Podocarp
Species listed under Appendix II CITES:
Prohibited Species Under Sabah Forest Enactment 1968:
Avian
At least 57 species of birds were recorded from this FR. The most specious families are Timaliidae (6) and Nectariniidae (6). Of which 8 species are Borneo endemic. Namely, i) Bornean Barbet, ii) Bornean Flowerpecker, iii) Pygmy-white eye, iv) Bornean Treepie, v) Chestnut-hooded Laughingthrust, vi) Bornean Whistler, vii) Red-breasted Patridge, and viii) Bornean Leafbird. Other interesting species that were recorded from this forest reserve are Bold-striped Tit Babbler and Plain Sunbird.
Insect
Twenty Bornean endemic insect species were recorded from this forest reserve.
Mammals
A total of 10 mammals’ species were recorded from this FR. The overall low count could be resulted of being a fragmented unit from a large forested landscape and also being surrounded by communities that protein sustenance came from wild bush meat. Of the 10 mammals recorded, one is cateogorised as Critically Endangered, namely the pangolin (Manis javanica), and one Near Threatened, namely the Bornean-Yellow Munctjak (Muntiacus antherodes). The former mammal is also listed as Schedule 1 (Totally Protected Species) under the Wildlife Conservation Enactment, 1997.
Illegal hunting – Wildlife, probably associated with easy access to the FR.
Strong community involvement on conservation and protection of nature capital in Winokok Conservation Area. This reserve is an important water catchment area for some rivers and a water source for Pekan Nabalu municipal water treatment plant.
FOREST RESEARCH CENTRE
MILE 14, JALAN SEPILOK
P.O.BOX 1407 90715
SANDAKAN SABAH
MALAYSIA
Tel: +6089 531522
Fax: +6089 531068
caims.sabah@gmail.com
The information in this site is intended solely for personal use by a user who accepts full responsibility for its use. While we have taken every precaution to ensure that the content of this site is both current and accurate, errors can occur.
The maps contained in this site should not be used for navigation purposes. In all cases, you should consult Sabah Forestry Department for advice concerning specific matters before making any conclusions related to information obtained from this site.
© 2024 CAIMS Sabah.