CLASS I PROTECTION
12,241.0 ha
Ranau
08.12.2016
41/109
–
None
Protection
Water sources for nearby settlements
Last updated: 31st October 2022
The FR is located 35 km south of Ranau and adjacent to Trus Madi FR (Class II Production Forest). The only road that is accessible to this area is via Kg Sinua.
Latitude/Longitude: 05° 33.084’ – 05° 43.215’N and 116° 33.197′ – 116° 41.600’E
Currently, there is no infrastructure established at the reserve.
Creations – The FR was gazetted as a Class I Protection Forest, covering an area of 12,241 ha in 2016. It was formerly part of the Trus Madi FR (Class II).
Management responsibility – Ranau District Forestry Office
Boundary matters – The boundary has not been demarcated.
Management plan – None
Current Use – Protection and research
Settlements and other buildings approximately 2 km from the boundary:
Topography
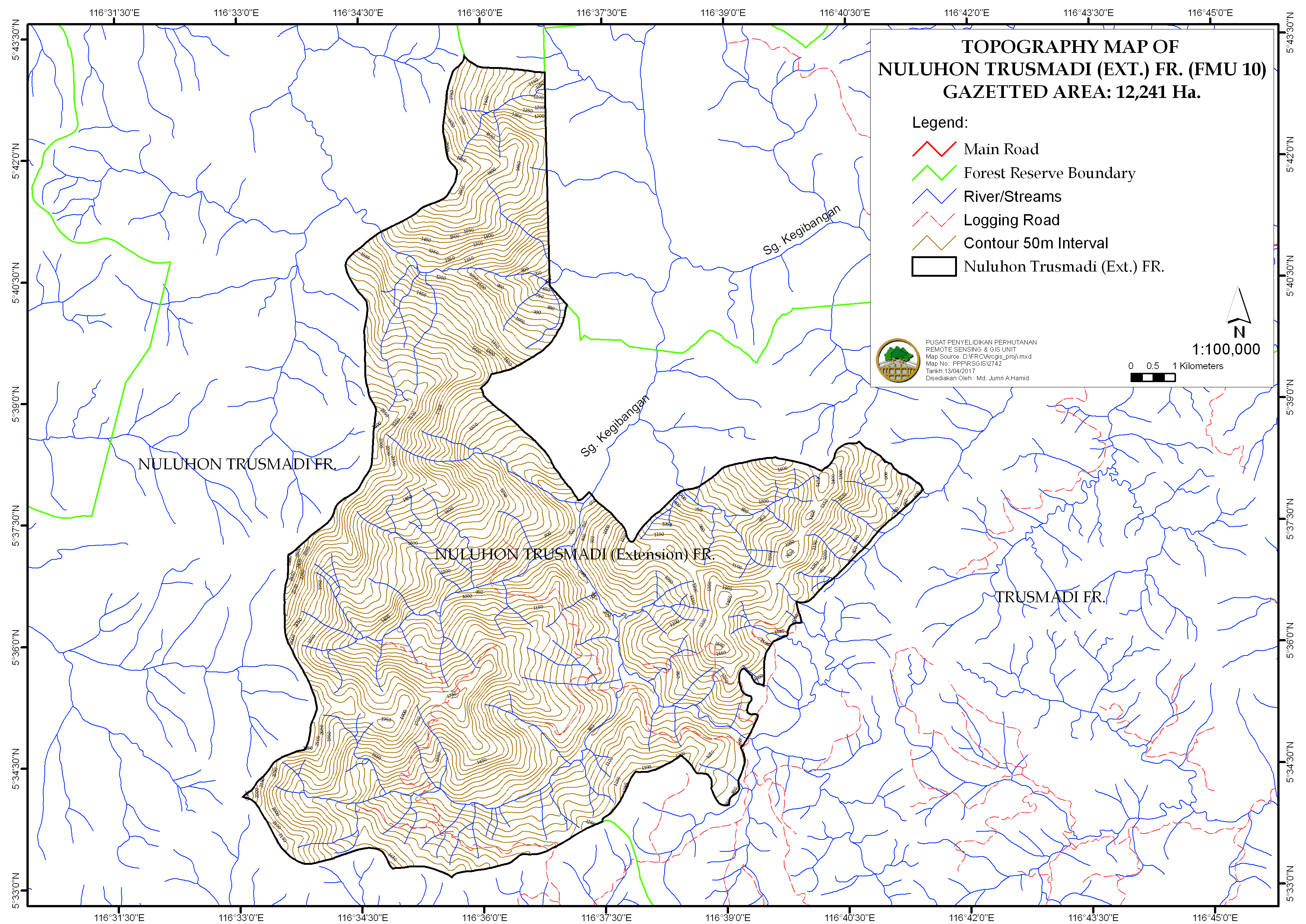
Figure 1: Topography and drainage map of Nuluhon Trusmadi (Extension) FR
Hydrology
Most of the tributaries of Pisa, Kanawan, Temerangan and Penulongan streams derived from the FR. These streams flow to the Kegibangan River, eventually joining the major Liwagu River.
Soils
Crocker, Lokan, and Trusmadi soil association.
Meteorological data
See Sinua rainfall data.
The upland mixed dipterocarp and lower montane forests predominantly covered the FR. However, anthropogenic disturbances in the past, such as timber extraction, result in the establishment of advanced-growth forests and secondary vegetations with various regenerative stages are now common. Fortunately, pristine montane vegetation covered the western steep mountainous ridges.
Flora
A total of 500 plant taxa were recorded from the reserve. The ten most speciose families in decreasing order are the Lauraceae (33), Rubiaceae (33), Melastomataceae (27), Myrtaceae (20), Fagaceae (18), Annonaceae (17), Meliaceae (17), Phyllanthaceae (17), Dipterocarpaceae (14) and Fabaceae (14). A total of 115 recorded taxa are endemic to Borneo, including 8 taxa endemic to Sabah. The diversity of oaks and chestnuts is high in the upland mixed dipterocarp and lower montane forests.
Threatened species under IUCN Red List:
Taxa under Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: –
Schedule 1, part II – (i) 2 Tetrastigma
Schedule 2, part II – (i) 8 Ginger (iii) Pitcher plants (iv) Rhododendron (v) Ramin
Species listed under Appendix II CITES:
Prohibited Species Under Sabah Forest Enactment 1968:
Avian
One hundred and five species from 43 families were recorded from this FR. The four most specious families are Pycnonotidae (10), Cuculidae (7), Timaliidae (7), Dicruridae (5), and Muscicapidae (4). Of the total taxa, 8 species are Bornean endemic, namely, Blue-banded Pitta, Bornean Barbet, Bornean treepie, Bornean-banded Pitta, Bornean-black Magpie, Bornean-leafbird, Bornean Brown Barbet and Chestnut-hooded laughingthrush.
Threatened species under IUCN Red List recorded from this FR include the Straw-headed Bulbul (CR), Greater-green Leafbird (EN), Grey-cheeked Bulbul (EN), Wrinkled Hornbill (EN), Crested Partridge (VU), Great Argus (VU), Great slaty Woodpecker (VU) and Sooty-capped Babbler (VU).
Insect
About 46 nocturnal species are recorded from the FR. At least 15 Bornean endemics were recorded from the 2017 survey. The endemics include four beetle species, five moth species, five dragonfly species and one stick insect species.
Mammals
A total of 17 mammal species from xx families were recorded from this FR.
Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: Schedule 1*; Schedule 2**; Schedule 3***
Forest fire — Drought-induced fire in the forest may change biomass stocks, impact plant and animal species functioning and alter the hydrological cycle.
Poaching — Illegal harvesting of natural resources.
Fragmentation — The loss, degradation or fragmentation of ecosystems through land conversion for agriculture, forest clearing and other forms of development.
Encroachment — Illegal clearing within the reserves.
The abundance of oaks and chestnuts found in the forest is an essential food source for wildlife besides a vital water catchment for surrounding communities.
FOREST RESEARCH CENTRE
MILE 14, JALAN SEPILOK
P.O.BOX 1407 90715
SANDAKAN SABAH
MALAYSIA
Tel: +6089 531522
Fax: +6089 531068
caims.sabah@gmail.com
The information in this site is intended solely for personal use by a user who accepts full responsibility for its use. While we have taken every precaution to ensure that the content of this site is both current and accurate, errors can occur.
The maps contained in this site should not be used for navigation purposes. In all cases, you should consult Sabah Forestry Department for advice concerning specific matters before making any conclusions related to information obtained from this site.
© 2024 CAIMS Sabah.