CLASS I PROTECTION
7,967.65 ha
Kota Marudu
08.12.2016
22/38
–
None
Protection
Wildlife corridor (Park & FR)
Last updated: 20th June 2022
The FR is located within the Kota Marudu District. The reserve shares approximately 5 km of its boundary with the Kinabalu Park in the west and eastern boundary with Lingkabau FR (Class II Commercial Forest). It is accessible from the Ranau-Kota Marudu road.
Latitude/Longitude: 6° 12.062’N–6° 17.258’N; 116° 45.222’E–116° 55.930’E
A highway road from Ranau to Kota Marudu was built traversing the reserve.
Creations – The FR was gazetted in 2016 as a Class I Protection Forest, covering an area of 7,967.65 ha. It was formerly part of the Lingkabau FR (Class II).
Management responsibility – Kota Marudu District Forestry Office
Boundary matters – The boundary is yet to be demarcated
Management plan – None
Current Use – Protection and Research
Settlements and other buildings approximately 2 km from the boundary:
This reserve’s northern and southern boundaries are adjacent to private land, mainly utilised for agricultural activities.
Topography
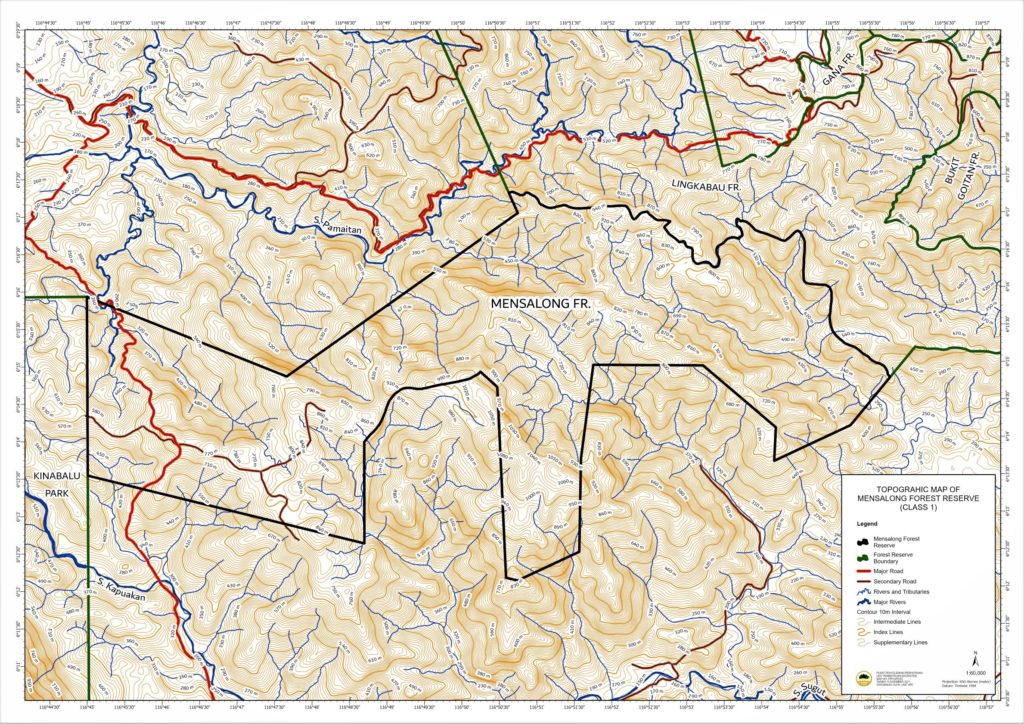
Hydrology
River tributaries: no information
Soils
Crocker soil associations
Meteorological data
See Tandek P.H rainfall data.
The original natural vegetation of Mensalong Forest Reserve is primarily covered with Mixed Dipterocarp Forest and a smaller extent of montane forest. However, anthropogenic disturbances in the past, such as timber extraction, encroachment and road development, has resulted in various quality and regenerative vegetation.
Flora
A total of 821 plant taxa were recorded from the reserve. The ten most speciose families in decreasing order are Rubiaceae (50); Lauraceae (45); Annonaceae (42); Dipterocarpaceae (34); Myrtaceae (32); Malvaceae (30); Euphorbiaceae (29); Fabaceae (29); Fagaceae (25); and Meliaceae (24).Of the total taxa recorded, 196 are endemics to Borneo, including 25 endemics to Sabah. 24 plant species are listed as threatened species under IUCN Red List.
Threatened species under IUCN Red List:
Taxa under Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: –
Schedule 1, part II – (i) Tetrastigma diepenhorstii (ii) Tetrastigma leucostaphylum
Schedule 2, part II – (i) 14 Gingers (ii) 6 Orchids (iii) 2 Ramin (iv) Agarwood (v) Fern
(vi) Palm
Species listed under Appendix II CITES:
Prohibited Species Under Sabah Forest Enactment 1968:
Avian
At least 101 species from 37 families of birds were recorded from this FR. Of which 10 species are Bornean endemic. Namely, i) Bornean Banded Pitta, ii) Bornean Ibon, iii) Bornean Spiderhunter, iv) Bornean Treepie, v) Chestnut-crested Yuhina, vi) Dusky Munia, vii) White-crowned Shama, viii) Black-throated Wren-babbler, ix) Blue-banded Pitta (VU) and x) Kinabalu Serpent Eagle (VU).
The most specious families are Pycnonotidae (13); Nectariniidae (8); Pellorneidae (8); Picidae (6); and Columbidae (5).
Insect
At least 76 insect species were recorded from this reserve. Nine species are endemic to Borneo, consisting of five moths, two beetles, and two damselflies.
Mammals
A total of 22 mammals’ species from 10 families were recorded from this FR.
Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: Schedule 1*; Schedule 2**; Schedule 3***
Illegal hunting – Wildlife, probably associated with easy access to the FR.
Road – hamper wildlife movement and pose the risk of wildlife roadkill.
Mensalong FR connects Kinabalu Park with other FRs, connecting two large forested areas. It should act as a wildlife corridor to facilitate wildlife movement. However, the newly built Ranau-Kota Maradu road that traverses the Mensalong FR could be a downside to this movement. More studies should be conducted in these areas.
FOREST RESEARCH CENTRE
MILE 14, JALAN SEPILOK
P.O.BOX 1407 90715
SANDAKAN SABAH
MALAYSIA
Tel: +6089 531522
Fax: +6089 531068
caims.sabah@gmail.com
The information in this site is intended solely for personal use by a user who accepts full responsibility for its use. While we have taken every precaution to ensure that the content of this site is both current and accurate, errors can occur.
The maps contained in this site should not be used for navigation purposes. In all cases, you should consult Sabah Forestry Department for advice concerning specific matters before making any conclusions related to information obtained from this site.
© 2024 CAIMS Sabah.