CLASS I PROTECTION
288.0 ha
Ranau
29.03.2012
29/44
–
None
Protection
Water catchment
Last updated: 7th July 2022
The Forest Reserve (FR) location is within the Ranau district. There are two main access roads into the reserve. Both access roads pass through villages, mainly Kg. Kepangian and Kg. Kinarasan. The other access road is no longer accessible.
Latitude/Longitude: 5° 51.749’N- 5° 52.984’N, 116° 36.734’E- 116° 38.002’E
Currently, there is no infrastructure established at the reserve.
Creations – The FR was initially gazetted in 2012, covering an area of 288 ha
Management responsibility – Ranau District Forestry Office
Boundary matters – The boundary has not been demarcated
Management plan – None
Current Use – Protection and Research
Settlements and other buildings approximately 2 km from the boundary:
Topography
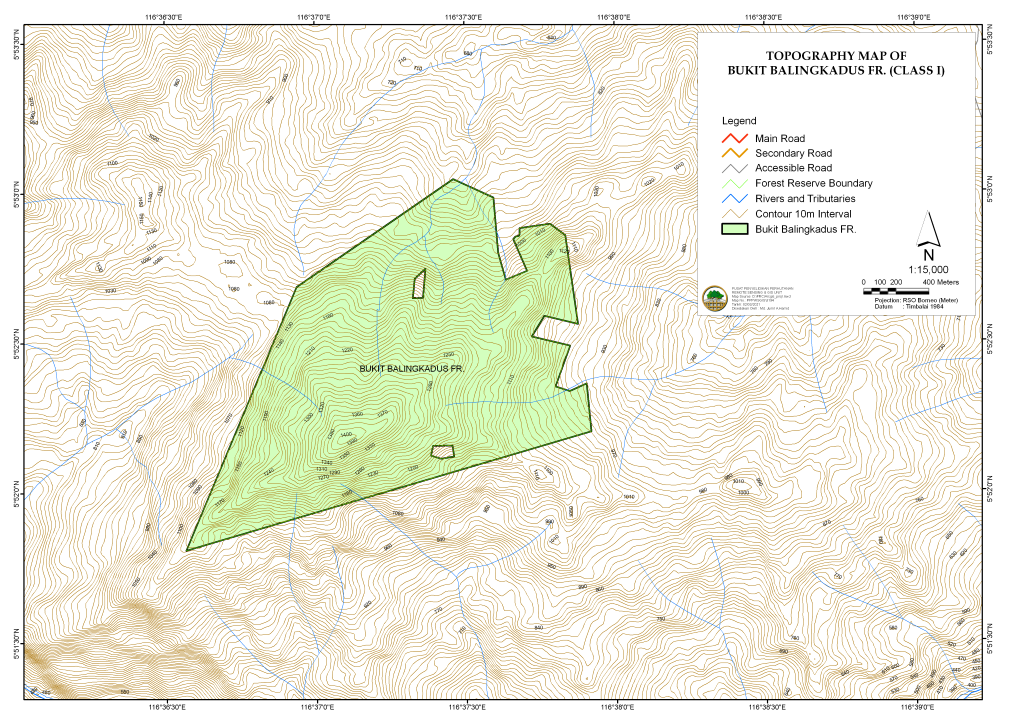
Figure 1: Topography and drainage map of Bukit Balingkadus FR
Hydrology
About five tributaries with a radial drainage pattern flow out from the reserve and feed the Melaut River and Liwagu River. The Melaut River will eventually join the Liwagu River.
Soils
Only Crocker soil associations are found in this forest reserve.
Meteorological data
See Ranau Agriculture Station rainfall data.
The upland mixed dipterocarp forest covered large area of the FR. In smaller extend, the lower montane vegetation is found on the topmost ridge of the hill. Anthropogenic disturbances are widespread and usually observed at the periphery of the reserves. These vegetation have degenerated into low diversity and structured secondary vegetation. The adjacent area are exposed to swidden agricultural systems (also known as shifting cultivation), rotational farming in which land is cleared by fire, cultivated and then left to regenerate after a few years. This farming method is practised for decades.
Flora
A total of 412 plant taxa were recorded from the reserve. The ten most speciose families in decreasing order are the Lauraceae (36), Rubiaceae (23), Myrtaceae (17), Annonaceae & Meliaceae (14), Melastomataceae (13), Fagaceae (12), Elaeocarpaceae & Phyllanthaceae (10), Apocynaceae & Clusiaceae (9), Euphorbiaceae, Moraceae & Sapotaceae (8) and Pentaphylacaceae & Sapindaceae (6). Of the total taxa recorded, 92 are endemic to Borneo, including 15 endemic to Sabah.
Threatened species under IUCN Red List:
Taxa under Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: –
Schedule 1, part II – (i) Rafflesia (ii) 2 Tetrastigma
Schedule 2, part II – (i) Orchid (ii) Ginger (iii) Pitcher plants (iv) Podocarpus (v) Ramin
Species listed under Appendix II CITES:
Prohibited Species Under Sabah Forest Enactment 1968:
Three high conservation value plant species, namely Agathis lenticula, Rafflesia cf. pricei and Vatica chartacea, are selected as part of the key conservation targets for monitoring biodiversity integrity in Bukit Balingkadus FR.
Avian
Eighty-six species from 37 families were recorded from this FR. The four most specious families are Pycnonotidae (10), Cuculidae (6), Megalaimidae (6), Columbidae (5), Eurylaimidae (4), and Nectariniidae (4). The most abundant bird families are Zosteropidae, Nectariniidae, Alcippeidae and Megalaimida. Of the total taxa, 13 species are Bornean endemic, namely, Blue-banded Pitta, Bornean Banded Pitta, Kinabalu Serpent Eagle, Bornean Barbet, Bornean Brown Barbet, Pale-faced Bulbul, Penan Bulbul White-crowned Shama, Bornean Green Magpie, Bornean Bulbul, Bornean Treepie, Chestnut-crested Yuhina and Dusky Munia.
Threatened species under IUCN Red List recorded from this FR include the Blue-banded Pitta (VU), Kinabalu Serpent Eagle (VU), Greater Green Leafbird (VU) and Wreathed Hornbill (VU).
Insect
About 95 nocturnal species are recorded from the FR and eight species are known as Bornean endemics. The endemics include seven moth species and two beetle species. Summary of insect sightings are as follows:
Mammals
A total of 12 mammals species from 10 families were recorded from this FR.
Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: Schedule 1*; Schedule 2**; Schedule 3***
Forest fire – Forest fire is a potential threat to the area due to entirely surrouded by agricultural landscape.
Poaching – Poaching of bush meat and plants is a potential threat due to easy access to the area.
The reserve is an essential water catchment for surrounding communities.
FOREST RESEARCH CENTRE
MILE 14, JALAN SEPILOK
P.O.BOX 1407 90715
SANDAKAN SABAH
MALAYSIA
Tel: +6089 531522
Fax: +6089 531068
caims.sabah@gmail.com
The information in this site is intended solely for personal use by a user who accepts full responsibility for its use. While we have taken every precaution to ensure that the content of this site is both current and accurate, errors can occur.
The maps contained in this site should not be used for navigation purposes. In all cases, you should consult Sabah Forestry Department for advice concerning specific matters before making any conclusions related to information obtained from this site.
© 2024 CAIMS Sabah.