CLASS I PROTECTION
1,300.3 ha
Ranau
24.08.2009
08.12.2016 (Ext.)
30.08.2017 (Ext. II)
21/25; 29/48; 29/51
–
None
Protection
Historical & Biodiversity Value
Last updated: 20th June 2022
The Forest Reserve (FR) is located within the Ranau district and adjacent to Kinabalu Park. There are three access roads into the reserve. The main access is by passing through the road to Ranau Sport Complex and Ranau Paragliding Park via the Ranau-Sandakan highway. The two other access roads, the old Mamut Copper Mine road and a bypass Kpg Lohan to Kpg Poring road are strictly for management used only.
Latitude/Longitude: 5° 59.045′ N-6° 1.698′ N, 116° 39.176′ E-116° 42.023′ E
A nature recreation centre is currently being develop under the federal development project of the 12th Malaysian Plan. The centre is located at the south-eastern part of the reserve (5° 59.702′ N, 116° 40.541’E).
Creations – The FR was initially gazetted in 2009, covering an area of 1,253 ha. Two extensions of the reserve were subsequently gazetted in 2016 and 2017 Bukit Hampuan Ext. (21 Ha) and Bukit Hampuan Ext. II (26.30 Ha), respectively. In total, the reserve covers an area of 1300.30 ha.
Management responsibility – Ranau District Forestry Office
Boundary matters – The boundary is yet to be demarcated
Management plan – None
Current Use – Protection and Research
Settlements and other buildings approximately 2 km from the boundary:
Settlements:
Facilities:
Topography
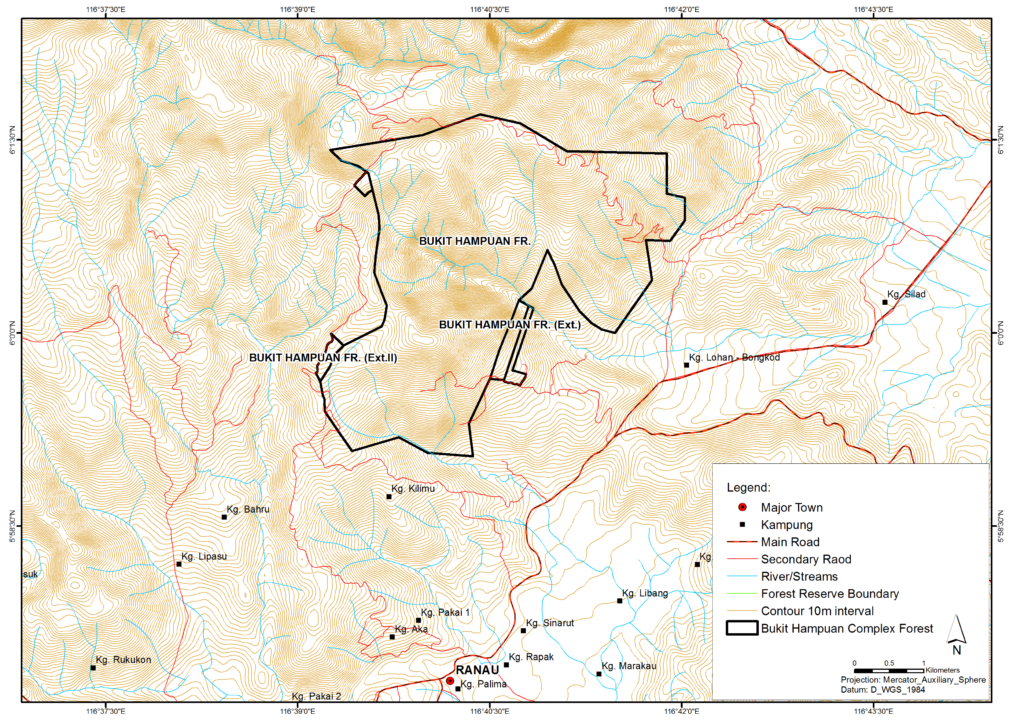 Figure 1: Topography and drainange map of Bukit Hampuan FR
Figure 1: Topography and drainange map of Bukit Hampuan FR
Hydrology
Major River: Lohan River
River tributaries:
Soils
Bidu-bidu, Dalit, Malubok, and Pinosuk soil associations
Meteorological data
See Ranau Agriculture Station rainfall data.
Originally, the forest ecosystems of the reserve was mainly classified as upland mixed dipterocarp forest and lower montane forest that established on Malubok and Pinosuk soil associations, and upland ultramafic forest and lower montane ultramafic forest on Bidu Bidu association. The forests have been subjected to various disturbances from timber extraction, wildfire and to some irreversible impact of mining. At present, disturbed upland mixed dipterocarp, lower montane and lower montane ultramafic forests, and various stages of secondary vegetations are the main vegetation classes in the reserve.
Flora
Physiographically, this reserve is connected and also forms part of Kinabalu highlands that mainly overlie on ultrabasic substrates. Hence, the forests harbour a multitude of endemic flora that are worth greater conservation attention. A total of 1,064 plant taxa were recorded from the reserve. The ten most speciose families in decreasing order are: Orchidaceae (81); Lauraceae (45); Rubiaceae (43); Fagaceae (41); Myrtaceae (41), Moraceae (34); Arecaceae (33), Annonaceae (28); Phyllanthaceae (26); and Meliaceae (24). Of the total taxa recorded, 288 are endemic to Borneo, including 60 endemic to Sabah and one as hyperendemic. The hyperendemic, Pittosporum linearifolium (Pittosporaceae) is so far only known from Bukit Hampuan area.
Threatened species under IUCN Red List:
Taxa under Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: –
Schedule 1, part II – (i) Rafflesia (ii) 4 Tetrastigma
Schedule 2, part II – (i) 81 Orchid (ii) 7 Gingers (iii) 6 Pitcher plants (iv) 4 Podocarps (v) 2 Ferns (vi) 1 Palm (vii) Ramin
Species listed under Appendix II CITES:
Prohibited Species Under Sabah Forest Enactment 1968:
Avian
Seventy-one species from 33 families were recorded from this FR. The six most specious families are Pycnonotidae (6), Columbidae (5), Megalaimidae (5), Nectariniidae (5), Timaliidae (5) and Pellorneidae (4). The most abundant bird families are Pycnonotidae, Nectariniidae and Zosterotidae.
Of which 10 species are Borneo endemic. Namely, Bornean Barbet, Bornean Flowerpecker, Bornean Leafbird, Bornean Swiftlet, Bornean Treepie, Chestnut-crested Yuhina, Crimson-headed Partridge, Dusky Munia, Mountain Barbet and White-crowned Shama.
Threatened species under IUCN Red List are Kinabalu Serpent Eagle (VU) and Wreathed Hornbill (VU).
Insect
Recorded up to 125 species at the lower montane forest (1,347 m a.s.l.). Nineteen Bornean endemic insect species were recorded, including one endemic to Bukit Hampuan.
Numbers of specimens are yet to be identified.
Mammals
A total of 16 mammals’ species from 10 families were recorded from this FR.
Wildlife Conservation Enactment 1997: Schedule 1*; Schedule 2**; Schedule 3***
Forest fire – Resulting from uncontrolled used of fire in agricultural practices.
Illegal hunting – Wildlife and orchids, probably associated with easy access to the FR.
Scenic view of Mt Kinabalu, other neigbouring mountains, i.e Mt Monkobo and Mt Mentapok, Ranau plain and the massive blue water lake of ex-mining pit of Mamut. Numerous attractive pitcher plants in opened area of Mamut Copper Mine. Beside these, Tandem Paragliding and hiking are established adventure sport attractions in Bukit Hampuan area.
FOREST RESEARCH CENTRE
MILE 14, JALAN SEPILOK
P.O.BOX 1407 90715
SANDAKAN SABAH
MALAYSIA
Tel: +6089 531522
Fax: +6089 531068
caims.sabah@gmail.com
The information in this site is intended solely for personal use by a user who accepts full responsibility for its use. While we have taken every precaution to ensure that the content of this site is both current and accurate, errors can occur.
The maps contained in this site should not be used for navigation purposes. In all cases, you should consult Sabah Forestry Department for advice concerning specific matters before making any conclusions related to information obtained from this site.
© 2024 CAIMS Sabah.